Vectors
A vector quantity has both length (magnitude) and
direction. The opposite is a scalar quantity, which only has magnitude. Vectors
can be denoted by AB, a, or AB (with an arrow above the
letters).
If a = (3) then the vector will look as follows:
(2)

NB1: When writing vectors as one number above another in
brackets, this is known as a column vector.
NB2: in textbooks and here, vectors are indicated by bold type. However, when
you write them, you need to put a line underneath the vector to indicate it.

Example:
If a = (-5) and b = ( 2), find the magnitude of their resultant.
( 3)
(1)
The resultant of two or more vectors is their sum.
The resultant therefore is (-3).
( 4)
The magnitude of this is ![]() (-3² + 4²) =
(-3² + 4²) = ![]() (9
+ 16) =
(9
+ 16) = ![]() (25) = 5
(25) = 5
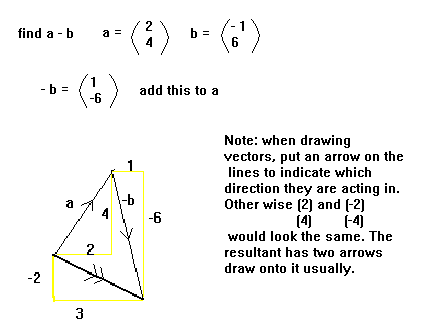
The addition and subtraction of vectors can be shown diagramatically. To find a
+ b, draw a and then draw b at the end of a. The
resultant is the line between the start of a and the end of b.
To find a - b, find -b (see above) and add this to a.
Example: